NICE is a deep learning framework changing high dimensional complex data into non linear independent components. This post summarizes the paper and explains some left out mathematical concepts especially why resulting jacobian of transformation function is unit constant, how to derive it and scaling of output layer. In addition, pytorch implementation of experimental results are given.
- Paper is arXiv:1410.8516
- Original code is fmu2/NICE/
Overview
Given data \(x \in \mathcal{X}^{D}\) is transformed using vector valued function of \(h=f(x)\) which is \(f: \mathcal{X}^{D} \to \mathcal{H}^{D}\) and trivially invertible. Distribution of \(h\) is assumed to be composed of independent components that can be factorized as follows:
\[P_{H}~(h) = \prod_{d \in \mathcal{D}}~P_{H_{d}}~(h_{d})\]Using change of variables, we obtain the following equation.
\[P_{X}~(x) = \underbrace{P_{H}~(f(x))}_\text{prior distribution} ~ \left \vert \det \frac{\partial f(x)}{\partial x} \right \vert \tag{1}\]To decide an \(f\) following two conditions should be met to benefit from NICE framework:
- Determinant of jacobian of f(x) such that \(J(f(x)) = \partial f(x) / \partial x\) is trivially obtained
- \(f^{-1}(h) = g(h)\) is also trivially obtained
As a result, learning criterion of NICE framework is maximizing the following log likelihood:
\[\log( P_{X}~(x)) = \sum_{d=1}^{\mathcal{D}} \log(P_{H_{d}}~(f_{d}(x))) + \log\left(\left \vert \det \frac{\partial f(x)}{\partial x} \right \vert \right) \tag{2}\]In the paper transformations are chosen to be additive coupling layers such that:
\(x = (x_{1}, x_{2}),~ h = (h_{1}, h{2})\) \(h_{1} = x_{1}\) \(h_{2} = x_{1} + m(x_{2}), \text{m is a neural network}\)
In subsequent sections, it will be shown that transformations using additive coupling result in unit constant determinant and hence make the equation (2) also constant if prior distribution is not learned. Therefore, to address the issue top layer is consequently scaled through using multiplicative coupling:
\[h = \exp(s) \odot h\]\(S\) is a diagonal matrix that scales the final outputs. At the end, learning criterion for settings having predetermined prior distribution and utilizing additive coupling with scaling becomes
\[\log( P_{X}~(x)) = \sum_{d=1}^{\mathcal{D}} \log(P_{H_{d}}~(f_{d}(x))) + \sum_{d=1}^{\mathcal{D}} |S_{ii}| \tag{3}\]Main points
- Every additive layer has unit determinant so top layer is a scaling diagonal \(S_{ii}\) matrix
- Paper uses isomorphic gaussian and logistic distribution so prior is not learned. In this case only thing left to learn is \(S_{ii}\) which indicates the important components
Experimental results
| Dataset | Preprocessing | Dimensions | Hidden layers | Hidden units | Prior | Log-likelihood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | None | 784 | 5 | 1000 | logistic | 1980 |
| TFD | Approx. whitening | 2304 | 4 | 5000 | gaussian | 5514 |
| SVHN | ZCA | 3072 | 4 | 2000 | logistic | 11496 |
| CIFAR-10 | ZCA | 3072 | 4 | 2000 | logistic | 5371 |
Mathematical background
Jacobians
The result of function compositions can be shown as \(h = f(x) = f_{L} ~ \circ \cdots f_{2} \circ f_{1}(x)\) and let’s show that jacobian of function compositions is equal to the matrix multiplication of individual function jacobians which is \(J(h) = \frac{\partial h}{\partial x} = \frac{\partial f_{L}}{\partial f_{L-1}} \cdots \frac{\partial f_{2}}{\partial f_{1}} \frac{\partial f_{1}(x)}{\partial x}\). we can demonstrate how the procedure works with an example and generalization can be derived building upon it. Functions and their depended variables are as follows:
\(h_{1} = f_{1}(x_{1}, x_{2}), ~~ h_{3} = f_{3}(h_{1}, h_{2})\) \(h_{2} = f_{2}(x_{1}, x_{2}), ~~ h_{4} = f_{4}(h_{1}, h_{2})\) \(h = (h_{3}, h_{4})\)
So jacobian of \(h\) is
\[J(h) = \frac{ \partial (h)}{\partial (x_{1}, x_{2})} = \frac{ \partial (h_{3},h_{4})}{\partial (x_{1}, x_{2})} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial x_{2} }\\ \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial x_{2} } \end{bmatrix} \tag{4}\]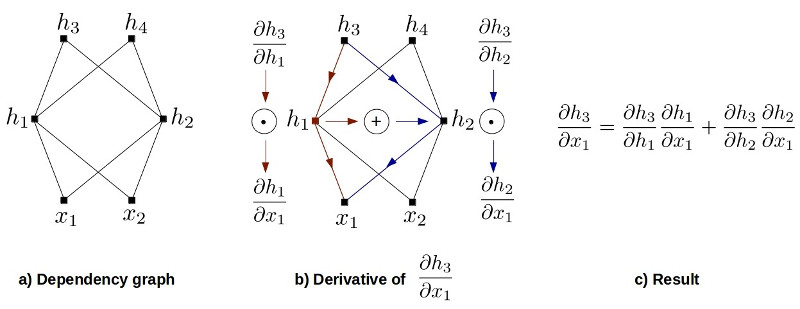
Figure 1 shows how to obtain partial derivative of a multivariable function with dependency graph of each function. If we plug results into (4), we end up with the following equation:
\[= \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{1}} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{1}} + \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{2}} \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{1}} & \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{1}} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{2}} + \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{2}} \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{2}} \\ \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{1}} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{1}} + \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{2}} \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{1}} & \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{1}} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{2}} + \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{2}} \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{2}} \end{bmatrix}\]We can decompose this expression using matrix multiplication such that
\[J(h) = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{2} }\\ \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{2} } \end{bmatrix} ~ \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{2} }\\ \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{2} } \end{bmatrix}\] \[J(h) = \frac{ \partial (h_{3},h_{4}) }{\partial (h_{1}, h_{2})} \frac{ \partial (h_{1},h_{2}) }{\partial (x_{1}, x_{2})} \tag{5}\]and finally since we are using the determinant of jacobian in (1), we can use \(\det(AB) = \det(A) \det(B)\) identity to find the result.
Coupling
Furthermore, we show why additive coupling generates unit constant determinant of jacobian by defining couping layers of transformation function as follows:
\(h_{1} =x_{1}\) \(h_{2} = x_{2} + m_{1}(x_{1})\) \(h_{3} = h_{1} + m_{2}(x_{2})\) \(h_{4} = h_{2}\) \(h = ( h_{3}, h_{4})\)
\[J(h) = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{3}}{\partial h_{2} }\\ \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{4}}{\partial h_{2} } \end{bmatrix} ~ \begin{bmatrix} \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{1}}{\partial x_{2} }\\ \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{1} } & \frac{ \partial h_{2}}{\partial x_{2} } \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} I_{d} & \frac{\partial m_{2}~(x_{2})}{ \partial h_{2}} \\ 0 & I_{d} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} I_{d} & 0 \\ \frac{\partial m_{1}~(x_{1})}{\partial x_{1}} & I_{d} \end{bmatrix}\]Another fact is that determinant of a triangular matrix is the multiplication of its diagonal elements and in this case the result is 1 due to identity matrices.
Whole library
Coding of library is pretty self explanatory and is added for exploratory purposes. Otherwise, library can be downloaded and imported as usual.
#Utility classes for NICE.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
#Additive coupling layer.
class Coupling(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_out_dim, mid_dim, hidden, mask_config):
"""Initialize a coupling layer.
Args:
in_out_dim: input/output dimensions.
mid_dim: number of units in a hidden layer.
hidden: number of hidden layers.
mask_config: 1 if transform odd units, 0 if transform even units.
"""
super(Coupling, self).__init__()
self.mask_config = mask_config
self.in_block = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_out_dim//2, mid_dim),
nn.ReLU())
self.mid_block = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(mid_dim, mid_dim),
nn.ReLU()) for _ in range(hidden - 1)])
self.out_block = nn.Linear(mid_dim, in_out_dim//2)
def forward(self, x, reverse=False):
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: input tensor.
reverse: True in inference mode, False in sampling mode.
Returns:
transformed tensor.
"""
[B, W] = list(x.size())
x = x.reshape((B, W//2, 2))
if self.mask_config:
on, off = x[:, :, 0], x[:, :, 1]
else:
off, on = x[:, :, 0], x[:, :, 1]
off_ = self.in_block(off)
for i in range(len(self.mid_block)):
off_ = self.mid_block[i](off_)
shift = self.out_block(off_)
if reverse:
on = on - shift
else:
on = on + shift
if self.mask_config:
x = torch.stack((on, off), dim=2)
else:
x = torch.stack((off, on), dim=2)
return x.reshape((B, W))
#Log-scaling layer.
class Scaling(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim):
"""Initialize a (log-)scaling layer.
Args:
dim: input/output dimensions.
"""
super(Scaling, self).__init__()
self.scale = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((1, dim)), requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, x, reverse=False):
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: input tensor.
reverse: True in inference mode, False in sampling mode.
Returns:
transformed tensor and log-determinant of Jacobian.
"""
log_det_J = torch.sum(self.scale)
if reverse:
x = x * torch.exp(-self.scale)
else:
x = x * torch.exp(self.scale)
return x, log_det_J
"""NICE main model.
"""
class NICE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, prior, coupling,
in_out_dim, mid_dim, hidden, mask_config):
"""Initialize a NICE.
Args:
prior: prior distribution over latent space Z.
coupling: number of coupling layers.
in_out_dim: input/output dimensions.
mid_dim: number of units in a hidden layer.
hidden: number of hidden layers.
mask_config: 1 if transform odd units, 0 if transform even units.
"""
super(NICE, self).__init__()
self.prior = prior
self.in_out_dim = in_out_dim
self.coupling = nn.ModuleList([
Coupling(in_out_dim=in_out_dim,
mid_dim=mid_dim,
hidden=hidden,
mask_config=(mask_config+i)%2) \
for i in range(coupling)])
self.scaling = Scaling(in_out_dim)
def g(self, z):
"""Transformation g: Z -> X (inverse of f).
Args:
z: tensor in latent space Z.
Returns:
transformed tensor in data space X.
"""
x, _ = self.scaling(z, reverse=True)
for i in reversed(range(len(self.coupling))):
x = self.coupling[i](x, reverse=True)
return x
def f(self, x):
"""Transformation f: X -> Z (inverse of g).
Args:
x: tensor in data space X.
Returns:
transformed tensor in latent space Z.
"""
for i in range(len(self.coupling)):
x = self.coupling[i](x)
return self.scaling(x)
def log_prob(self, x):
"""Computes data log-likelihood.
(See Section 3.3 in the NICE paper.)
Args:
x: input minibatch.
Returns:
log-likelihood of input.
"""
z, log_det_J = self.f(x)
log_ll = torch.sum(self.prior.log_prob(z), dim=1)
return log_ll + log_det_J
def sample(self, size):
"""Generates samples.
Args:
size: number of samples to generate.
Returns:
samples from the data space X.
"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
z = self.prior.sample((size, self.in_out_dim)).cuda()
else:
z = self.prior.sample((size, self.in_out_dim)).cpu()
return self.g(z)
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass.
Args:
x: input minibatch.
Returns:
log-likelihood of input.
"""
return self.log_prob(x)
#Utility functions for NICE.
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def dequantize(x, dataset):
'''Dequantize data.
Add noise sampled from Uniform(0, 1) to each pixel (in [0, 255]).
Args:
x: input tensor.
reverse: True in inference mode, False in training mode.
Returns:
dequantized data.
'''
noise = torch.distributions.Uniform(0., 1.).sample(x.size())
return (x * 255. + noise) / 256.
def prepare_data(x, dataset, zca=None, mean=None, reverse=False):
"""Prepares data for NICE.
In training mode, flatten and dequantize the input.
In inference mode, reshape tensor into image size.
Args:
x: input minibatch.
dataset: name of dataset.
zca: ZCA whitening transformation matrix.
mean: center of original dataset.
reverse: True if in inference mode, False if in training mode.
Returns:
transformed data.
"""
if reverse:
assert len(list(x.size())) == 2
[B, W] = list(x.size())
if dataset in ['mnist', 'fashion-mnist']:
assert W == 1 * 28 * 28
x += mean
x = x.reshape((B, 1, 28, 28))
elif dataset in ['svhn', 'cifar10']:
assert W == 3 * 32 * 32
x = torch.matmul(x, zca.inverse()) + mean
x = x.reshape((B, 3, 32, 32))
else:
assert len(list(x.size())) == 4
[B, C, H, W] = list(x.size())
if dataset in ['mnist', 'fashion-mnist']:
assert [C, H, W] == [1, 28, 28]
elif dataset in ['svhn', 'cifar10']:
assert [C, H, W] == [3, 32, 32]
x = dequantize(x, dataset)
x = x.reshape((B, C*H*W))
if dataset in ['mnist', 'fashion-mnist']:
x -= mean
elif dataset in ['svhn', 'cifar10']:
x = torch.matmul((x - mean), zca)
return x
#Standard logistic distribution.
class StandardLogistic(torch.distributions.Distribution):
def __init__(self):
super(StandardLogistic, self).__init__()
def log_prob(self, x):
"""Computes data log-likelihood.
Args:
x: input tensor.
Returns:
log-likelihood.
"""
return -(F.softplus(x) + F.softplus(-x))
def sample(self, size):
"""Samples from the distribution.
Args:
size: number of samples to generate.
Returns:
samples.
"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
z = torch.distributions.Uniform(0., 1.).sample(size).cuda()
else:
z = torch.distributions.Uniform(0., 1.).sample(size).cpu()
return torch.log(z) - torch.log(1. - z)
Train example
- 4 different data sets are included:
"mnist","fashion-mnist","svhn"and"cifar10". - If
save_model_and_load = True, then next training session starts with previous information of neural network. - If gpu support is not present, it really takes a long time to train, so colab might be more preferable.
import torch, torchvision
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
dataset_choice = "mnist" # Other possible parameters: "fashion-mnist", "svhn", "cifar10".
max_iter = 1 # Around 4000 pictures start to have discernible shapes.
save_model_and_load = True # If "True" trained model is saved and loades in every run.
def main(args):
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
# model hyperparameters
dataset = args.dataset
batch_size = args.batch_size
latent = args.latent
max_iter = args.max_iter
sample_size = args.sample_size
coupling = 4
mask_config = 1.
# optimization hyperparameters
lr = args.lr
momentum = args.momentum
decay = args.decay
zca = None
mean = None
if dataset == 'mnist':
mean = torch.load('./NICE/statistics/mnist_mean.pt')
(full_dim, mid_dim, hidden) = (1 * 28 * 28, 1000, 5)
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
trainset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='~/torch/data/MNIST',
train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
elif dataset == 'fashion-mnist':
mean = torch.load('./statistics/fashion_mnist_mean.pt')
(full_dim, mid_dim, hidden) = (1 * 28 * 28, 1000, 5)
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
trainset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root='~/torch/data/FashionMNIST',
train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
elif dataset == 'svhn':
zca = torch.load('./statistics/svhn_zca_3.pt')
mean = torch.load('./statistics/svhn_mean.pt')
(full_dim, mid_dim, hidden) = (3 * 32 * 32, 2000, 4)
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
trainset = torchvision.datasets.SVHN(root='~/torch/data/SVHN',
split='train', download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
elif dataset == 'cifar10':
zca = torch.load('./statistics/cifar10_zca_3.pt')
mean = torch.load('./statistics/cifar10_mean.pt')
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
torchvisitransforms.ToTensor()])
(full_dim, mid_dim, hidden) = (3 * 32 * 32, 2000, 4)
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='~/torch/data/CIFAR10',
train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
if latent == 'normal':
prior = torch.distributions.Normal(
torch.tensor(0.).to(device), torch.tensor(1.).to(device))
elif latent == 'logistic':
prior = StandardLogistic()
filename = '%s_' % dataset \
+ 'bs%d_' % batch_size \
+ '%s_' % latent \
+ 'cp%d_' % coupling \
+ 'md%d_' % mid_dim \
+ 'hd%d_' % hidden
flow = NICE(prior=prior,
coupling=coupling,
in_out_dim=full_dim,
mid_dim=mid_dim,
hidden=hidden,
mask_config=mask_config).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(
flow.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(momentum, decay), eps=1e-4)
if save_model_and_load:
PATH = './models/' + filename + 'last.tar'
if os.path.exists('./models') and os.path.isfile(PATH):
checkpoint = torch.load(PATH)
flow.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_state_dict'])
total_iter = 0
train = True
running_loss = 0
while train:
for _, data in enumerate(trainloader, 1):
flow.train() # set to training mode
if total_iter == max_iter:
train = False
break
total_iter += 1
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradient tensors
inputs, _ = data
inputs = prepare_data(
inputs, dataset, zca=zca, mean=mean).to(device)
# log-likelihood of input minibatch
loss = -flow(inputs).mean()
running_loss += float(loss)
# backprop and update parameters
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if total_iter == max_iter or total_iter % 10 ==0:
mean_loss = running_loss / total_iter
bit_per_dim = (mean_loss + np.log(256.) * full_dim) \
/ (full_dim * np.log(2.))
print('iter %s:' % total_iter,
'loss = %.3f' % mean_loss,
'bits/dim = %.3f' % bit_per_dim)
running_loss = 0.0
flow.eval() # set to inference mode
with torch.no_grad():
z, _ = flow.f(inputs)
samples = flow.sample(sample_size).cpu()
samples = prepare_data(
samples, dataset, zca=zca, mean=mean, reverse=True)
npimg = torchvision.utils.make_grid(samples).numpy()
plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1,2,0)))
print('Finished training!')
if not os.path.exists('./models'):
os.makedirs('./models')
torch.save({
'total_iter': total_iter,
'model_state_dict': flow.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer.state_dict(),
'dataset': dataset,
'batch_size': batch_size,
'latent': latent,
'coupling': coupling,
'mid_dim': mid_dim,
'hidden': hidden,
'mask_config': mask_config},
'./models/' + filename +'last.tar')
print('Checkpoint Saved')
class Args():
def __init__(self, dataset, batch_size, latent, max_iter, sample_size=64, lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, decay=0.999):
self.dataset = dataset
self.batch_size= batch_size
self.latent = latent
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.sample_size = sample_size # number of images to generate
self.lr = lr # learning rate
self.momentum= momentum # beta1 in Adam optimizer
self.decay = decay # beta2 in Adam optimizer.
if dataset_choice == "mnist":
args = Args(dataset="mnist", batch_size=200, latent="logistic",max_iter=max_iter)
if dataset_choice == "fashion-mnist":
args = Args(dataset="fashion-mnist", batch_size=200, latent="logistic",max_iter=max_iter)
if dataset_choice == "svhn":
args = Args(dataset="svhn", batch_size=200, latent="logistic",max_iter=max_iter)
if dataset_choice =="cifar10":
args = Args(dataset="cifar10", batch_size=200, latent="logistic",max_iter=max_iter)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(args)